Breastfeeding physiology
The hormones mainly involved in breastfeeding are prolactin, which causes milk to be made, and oxytocin, which causes it to be excreted.
After childbirth, prolactin levels rise and remain high for months, and it is with the expulsion of the placenta that milk production begins. In addition, prolactin peaks are made each time the baby breastfeeds and in response to breast stimulation; that is, if the child breastfeeds a lot, there will be a lot of prolactin and therefore a lot of milk.
Oxytocin causes the contraction of several muscle fibers, including those in the areola of the chest. Usually, at the beginning of breastfeeding, you notice a tingling sensation in the breast, as the milk comes out: it is the so-called ejection reflex.
There is also a hormone that acts locally to control the secretion of milk. It is called FIL (Breastfeeding Inhibitor Factor) and is an inhibitor of milk production. If the baby sucks a lot, she takes the FIL and produces more milk, while if the baby sucks a little, the inhibitor stays inside the breast and makes little milk.
Milk production is adjusted automatically, from one intake to the next and independently for each breast, according to the needs of the baby.
A few months after delivery, prolactin decreases, but the volume of milk produced does not, but increases according to demand thanks to this local action of the FIL.
Why breastfeed?
Breast milk is the best food for the baby during the first 6 months of life, because it covers all your nutritional needs and adapts to your limited digestive and metabolic capacity.
Advantages for the mother:
- Postpartum uterine recovery and decreased bleeding.
- Improved anemia and increased iron reserves.
- Weight loss and silhouette recovery.
- Decreased risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
- Decreased likelihood of hip and spine fractures in post menopause.
- Economic savings (you don't need special utensils; less illness in children, therefore less spending on medicines, hospital stays and medical visits; less absenteeism from parents).
- Psychological benefits (oxytocin decreases stress response; breastfeeding is important for the development of a healthy emotional bond; pleasant; less postpartum depression)
The first 6 months: exclusive breastfeeding. Because?
- It brings benefits for both mother and baby.
- It has no adverse effects on infant growth.
- Protects against intestinal infections.
- It increases, in many cases, the time of amenorrhea (time without menstruation).
- Promotes greater maternal weight loss after childbirth.
Lactation on demand
Most babies are awake for the first 2-4 hours after birth, only to go into a state of drowsiness that can last 12 hours. For that, it is important to take advantage of the first moments after birth to put the baby to the breast.
- Different studies show that the breastfeeding on demand improves weight recovery after birth, decreases jaundice (yellowish coloration) in the first days, and increases the duration of breastfeeding.
- Schedule on demand is recommended from the beginning.
- From 24 hours of life, the baby should make at least 8-10 shots a day.
- The duration of the shots should not be limited.
- Most babies make short, frequent shots on the first day; however, they are perfectly effective in stimulating the rise of milk.
- As the days go by, the baby’s sense of hunger increases, and therefore the duration of the prey.
- The gradual increase in mother's milk production favors the baby's satiety, which will again limit the duration of the intake.
- It is recommended that the baby is always by the mother's side during the hospital stay:
- Breastfeeding on demand is only possible if the baby is constantly or as long as possible with his mother. It has been shown to be accompanied by increased breastfeeding success.
- Facilitates health education by nursing staff
- It allows parents to become familiar with their baby, decreasing anxiety when discharged.
- It is important encourage the mother to rest. By breastfeeding on demand, it is recommended to take the opportunity to rest and sleep the moments when the baby also does so. Excessive visits in the first days make this possibility difficult and can also interfere with breastfeeding on demand.
- The physical contact with the baby. Many babies who cry often in the first few days calm down by placing them on their chest or by physical contact with their mother or father. The family bed (sharing the bed with the baby, colecho) promotes breastfeeding on demand and also the rest of the mother and baby.
Preservation of breast milk
Hygienic measures
Wash your hands thoroughly before extracting the milk.
Use glass or hard plastic containers for food use, previously washed with hot soapy water, or disposable plastic bags specially made for storing breast milk.
Mark the containers with the date of milk extraction.
Refrigerate or freeze milk as soon as possible.
If you are pumping milk out of the house, keep it in the fridge, and use a portable fridge or isothermal bag to move the milk.
It is advisable to store breast milk in small quantities to facilitate thawing.
Milk preservation
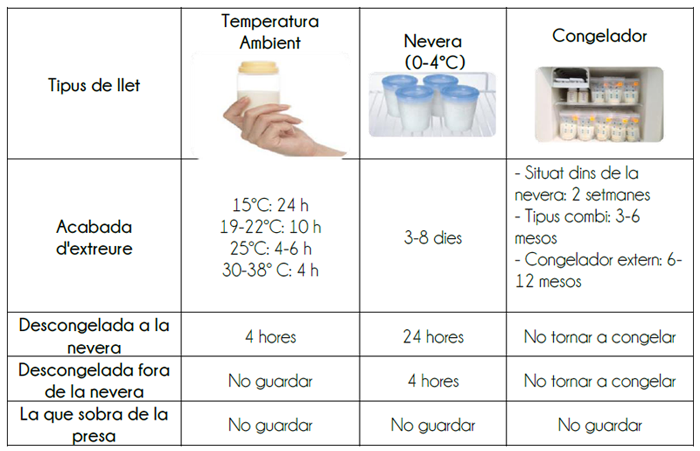
How to thaw breast milk
- Older milk should be used first.
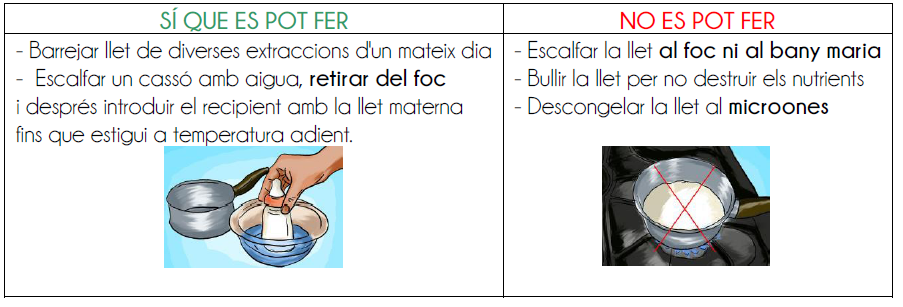
- Ideally, thaw it in the refrigerator the day before. If this is not possible, place the container with the frozen milk under the tap, starting with the warm water and go hot until it reaches the right temperature. You can also heat a saucepan with water and then fill the container with frozen milk (more environmentally friendly).
- Once thawed, the milk may have a sour smell; this odor is attributed to a change in the structure of the lipids, not that it is in poor condition. Do not throw away milk for this reason.
How to heat breast milk
- The baby can drink milk at room temperature or heated.
- You can use a bottle warmer.
- Heat a saucepan with water, remove from the heat and then fill the container with breast milk until it is at the right temperature.
- If you heat the milk in the microwave, it is important to mix it well and test that it is at the right temperature to avoid burning the baby.
Importance of colostrum
Colostrum or first milk is a thick secretion, which can be transparent or yellowish, which begins to produce in the middle of pregnancy and is excreted during the first days of postpartum.
Colostrum is the ideal nutrient for our baby as it contains many proteins, especially immunoglobulins, which provide a very important dose of defenses against viral and bacterial infections. In addition, it is rich in vitamin A (this vitamin plays a very important role in the baby's visual development) vitamin E, K, beta-carotene and minerals such as sodium and zinc.
Through colostrum the mother also gives her child large amounts of white blood cells that help prevent infections.
Stimulation of breastfeeding
There are times when it is not possible to start breastfeeding immediately after birth because the baby has had to be admitted to the neonatal unit for some reason such as prematurity. In these cases it is very important start to stimulate the chest as soon as possible in order to start colostrum production.
In order to initiate the stimulation of breastfeeding we can do it in two ways: with manual extraction or with the help of an electric or manual tug.
Manual extraction
It is the most similar form to the extraction that the baby does, and consists of a sequence of massages on the mammary gland to encourage the outflow of milk through the nipple.
It is ideal for the first days when large amounts of milk should not be extracted. It is normal that the first times you perform the manual extraction you extract very little amount. With practice you will see how you extract more and more.
Electric or manual pull
It can be more useful when we need to do more frequent extractions and to extract more milk. Is important, whether we use a manual puller or an electric one, do the sequence of massages on the mammary gland explained in the manual extraction, in order to achieve a good extraction.

Breastfeeding support groups
They are postpartum and breastfeeding support groups. Ask your area midwife (CAP).
Some of them are:
- Mom. Cerdanyola del Vallès
Wednesday, 11 a.m. to 12.30:XNUMX p.m.
C /. Tort, 17, Cerdanyola.
Tel. +722 232
This e-mail address is being protected from robots spam.Necessites Javascript enabled to view it.
Also groups of pregnant women and children. - Sea of milk. Ripollet
Every Monday from 10am to 12pm.
Ripollet Cultural Center. Rambla St. Jordi, 2-4, Ripollet.
Tel. 685 649 879 - 93 592 10 47
This e-mail address is being protected from robots spam.Necessites Javascript enabled to view it. - Mamas Santa Perpetua. Santa Perpetua de la Mogoda.
Wednesday, 15 to 16.30:XNUMX p.m.
Can Folguera Civic Center. C / Pablo R. Picasso, 32. Santa Perpètua de la Mogoda
Tel +93 574 06 81
Tel. Emergencies: 619 49 40 02 - From 15 pm to 17 pm, on working days. - Hugs (Facebook). Sant Cugat del Vallès
Every school Thursday, from 11 a.m. to 13 p.m.
Black Chalet. Plaça del Coll, 4. Sant Cugat.
Also parenting groups and play space for 0-3 year olds. - Gift of mother. Terrace
Monday, from 18pm to 19.30pm.
Sant Pere Neighborhood House. Paseo 22 de Julio, 337. Terrace.
Tel. Emergencies: 680 415 067 (Esther Guerrero) and 645 792 897 (Marina Albiñana) - Dawn Breastfeeding
Tel. Emergencies: 690 144 500
Breast milk donation
Documents and resources of interest
- Breastfeeding: Information and support to promote breastfeeding. Women's Area. Parc Taulí University Hospital.
- e-lactation. Medication and breastfeeding.
From this website you can check the compatibility of any medication with breastfeeding.
- What you need to know: Breastfeeding. Virtual Nurse.