The classification of the parts is based on different factors. Part type according to:
According to medical interventions
- Normal. It is the only physiological process in which a woman ends a gestation (between 37 and 42 weeks of gestation) and involves psychological and socio-cultural factors. It starts spontaneously, develops and ends without complications, culminates in birth and does not involve interventions beyond a comprehensive and respectful support (Federation of Matron Associations of Spain 2006).
- Medicalized (intervened). This is what is produced vaginally, preceded by interventions such as artificial rupture of membranes (artificial amniorrexis or rupture of the pouch),peridural anesthesia, episiotomy, induction (provocation) or acceleration by synthetic hormones such as oxytocin or prostaglandins.
"According to medical interventions," d'Virtual Nurse, content under license CC BY-NC-ND 3.0 ES
Depending on the duration of the pregnancy
- Part out. This occurs between 37 and 42 weeks of gestation.
- Part preterme me. This is what occurs before the 37th week of gestation.
-
Part postterm. This is what happens beyond the 42nd week of gestation
"Depending on the duration of the pregnancy," d'Virtual Nurse, content under license CC BY-NC-ND 3.0 ES
Depending on the finish
- Eutocytic part. This is what occurs vaginally and in which the fetus is born from the head and without the need to resort to any extractor or special manipulations. In the literature, concepts related to eutocytic birth, such as the, can also be found part in the water, childbirth without pain, soft childbirth, humanized childbirth, conscious childbirth or natural childbirth, according to different social trends and in the conception of health.
-
Dystrophic part. This requires special intervention and instrumentation before the baby is born. As well, it can be classified in:
- surgical part, in which the birth occurs with a surgery called cesarean section;
- instrumental part, in which the birth occurs vaginally through the use of instruments such as forceps, spatulas or the suction cup.
"Depending on the finish," d'Virtual Nurse, content under license CC BY-NC-ND 3.0 ES
Depending on the cause of the risk
-
Childbirth after a caesarean section. The pregnant woman who has had a cesarean section may give birth vaginally. In this case, the reason for the previous caesarean section should be evaluated, and the use of stimulating or inducing labor drugs should be carried out with special care because of the risk of uterine scar dehiscence.
-
Part of the buttocks or pelvis. At the end of pregnancy, the fetus may be placed on its buttocks, i.e. instead of presenting the fetal head in the starting position (in the upper strait of the maternal pelvis) it has the buttocks and / or the lower extremities. Between 3% and 4% of pregnancies end with presentation of buttocks.
The professionals at your hospital will tell you about the different options for attending birth in these cases.
In some hospitals, there are protocols that allow the woman to return to the fetus through the abdominal cavity at week 37 of gestation - this maneuver is called an external version. At other centers, each case is evaluated individually and aspects such as first birth, estimated fetal weight, fetal head position (using an abdominal x-ray), etc. are taken into account.
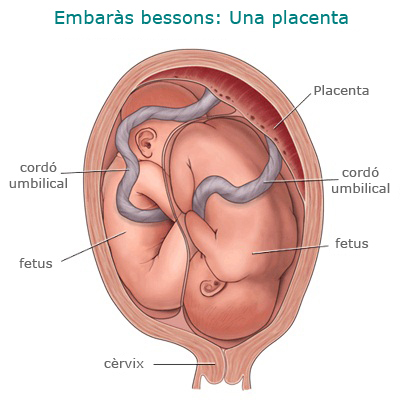
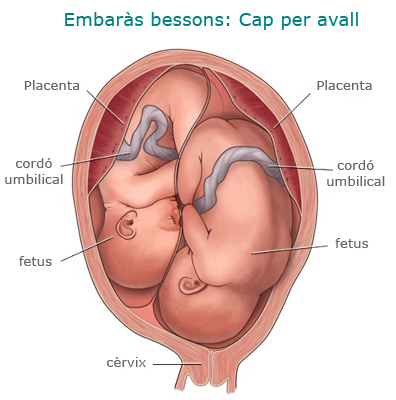
- Part of twins. The route of delivery in twin pregnancies depends on fetal static (i.e., fetal placement), gestational age, and fetal weights. In any case, the birth of twins is considered high risk; therefore, they are recommended continuous monitoring of fetal well-being and peridural anesthesia to be able to act quickly in case of complications during labor.
If both fetuses are in a cephalic, head-to-head position, vaginal delivery is recommended: after the birth of the first twin, the second bag is ruptured and always under continuous heart rate monitoring. fetal birth is expected.
 Source: http: www.childrenscentralcal.org/HealthE/PublishingImages/sm_1866.gif
Source: http: www.childrenscentralcal.org/HealthE/PublishingImages/sm_1866.gif
If the first fetus is placed head and the second, in another presentation, the way to end the delivery depends on the gestational age and the fetal weight. At gestations below 32 weeks or weights below 1.500 g, caesarean section is recommended; in gestations above 32 weeks and weights above 1.500 g, vaginal delivery may be attempted. In any other case it is indicated to end the pregnancy by cesarean section. -
Source: http: www.childrenscentralcal.org/HealthE/PublishingImages/sm_1866.gif
- Risk part for maternal or fetal illness. In some exceptional situations, it may be advisable to terminate the pregnancy in one way or another depending on the maternal or fetal status. Some maternal illnesses, such as those that require changes in medication at birth (women undergoing anticoagulant treatment) or stabilization (women with heart disease or preeclampsia), indicate termination of labor through induction, before it is delivered. There are also other problems related to the fetus, such as delayed intrauterine growth, which can trigger an induction of labor before gestation. In other cases, such as with premature birth, uterine fibroids in the lower uterine or cervical region, or more than two previous uterine interventions, maternal or fetal pathology does not allow for vaginal delivery and pregnancy must be terminated. by cesarean section.
"Depending on the cause of the risk", d'Virtual Nurse, content under license CC BY-NC-ND 3.0 ES, with modifications made by the Gynecology and Obstetrics Service of the Hospital de Sabadell